Imagine having a tool that helps you visually understand the complexities of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) at a glance. This is what an Autism Spectrum Disorder graph offers.
You might find yourself overwhelmed by endless information and jargon when trying to comprehend ASD. With this graph, you can simplify the chaos. It turns intricate data into clear visuals, making it easier for you to grasp and relate to.
As you dive deeper into this article, you’ll discover how this powerful tool can transform your understanding and approach to ASD. Ready to unlock insights that could make a real difference in your life or someone you care about? Let’s get started.
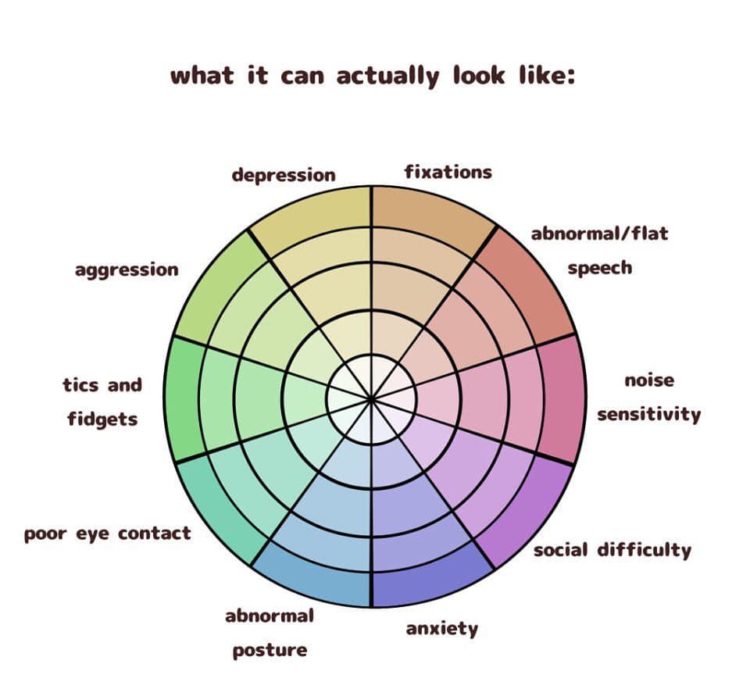
Credit: themighty.com
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) affects individuals in diverse ways. Understanding ASD is essential for fostering empathy and support. This section explores key aspects of ASD through defining characteristics, prevalence, and its impact on individuals.
Defining Characteristics
ASD is a developmental disorder with varying symptoms. Common signs include difficulty in communication and social interaction. Many individuals have repetitive behaviors or specific interests. Each person with ASD is unique in their challenges and strengths.
Prevalence And Statistics
ASD occurs across all ethnic and socioeconomic groups. Recent studies show an increase in ASD diagnoses. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates 1 in 54 children are diagnosed with ASD. Early diagnosis and intervention can help manage symptoms effectively.
Impact On Individuals
ASD affects daily life in significant ways. Individuals may face challenges in social settings or routine tasks. Supportive environments and tailored strategies can enhance their quality of life. Many people with ASD excel in specialized skills or areas of interest.

Credit: www.thekeyschool.org
Importance Of Visual Data
Visual data plays a vital role in understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder. Graphs and charts provide clarity. They help in digesting complex information. With visual aids, patterns become evident. Researchers and educators find them indispensable. They bridge the gap between raw data and comprehension. Visual data fosters communication among non-experts. This can enhance public awareness. It also aids in informed decision-making. In the realm of autism research, their importance is undeniable.
Role Of Graphs In Autism Research
Graphs simplify complicated datasets. They present data in a straightforward way. Researchers use them to track progress and trends. Autism studies often involve extensive data collection. Graphs help visualize behaviors and interventions. They highlight changes over time. This is crucial for evaluating therapies. Graphs also assist in identifying patterns. These patterns may lead to new insights. Visual representation can inspire further research. It acts as a catalyst in scientific exploration.
Enhancing Comprehension Through Visualization
Visualization makes learning easier. Graphs convert numbers into visual stories. This aids in better understanding. Readers grasp information quickly. Visual data reduces cognitive load. It transforms complex details into digestible snippets. This is essential for non-experts. Parents and educators benefit from clear visuals. They can make informed choices for children with autism. Visualization fosters meaningful discussions. It encourages engagement and curiosity. Everyone can access valuable insights effortlessly.
Types Of Graphs Used
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) requires analyzing diverse data sets. Graphs play a crucial role in visualizing this data. Different types of graphs help in understanding various aspects of ASD. Each graph type offers unique insights. They make complex data understandable.
Bar Graphs For Comparative Analysis
Bar graphs are simple yet effective. They compare data across categories. Each bar represents a different group. The height shows the value. This makes it easy to spot differences. For ASD, bar graphs can compare prevalence rates. They show variations across regions or age groups. They help identify areas needing attention.
Line Graphs For Trends Over Time
Line graphs are great for showing trends. They track changes over periods. A line connects data points across time. This visualizes the progression. In ASD studies, line graphs reveal changes in diagnosis rates. They highlight increases or decreases over years. They show the impact of interventions.
Pie Charts For Demographic Insights
Pie charts break down data into parts. Each slice represents a percentage. They give a snapshot of composition. In ASD demographics, pie charts show age distribution. They depict gender ratios among diagnosed individuals. This helps in understanding the population affected. It aids in tailoring specific interventions.
Key Visual Insights
Autism Spectrum Disorder Graphs highlight patterns and trends in autism diagnosis. They offer clear visual insights into prevalence and growth over time. Understanding these graphs helps in grasping the complexity and distribution of autism across different demographics.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) through visual data can be a powerful way to grasp its complexities. Graphs provide a clear, concise representation of intricate data, allowing you to identify trends and correlations that might be missed in text-heavy reports. Let’s dive into some key visual insights that can help you better understand ASD.
Patterns In Asd Diagnosis
ASD diagnosis patterns often reveal fascinating trends. For instance, many graphs show a steady increase in diagnoses over the past decades. This could suggest improved awareness and better diagnostic tools rather than an actual rise in cases. A personal observation: when my nephew was diagnosed, the process was much more straightforward than it was for my cousin ten years earlier. Such advancements highlight the importance of visual data in tracking progress. Have you noticed similar trends in your community? Observing these patterns can prompt questions about access to healthcare and education.
Correlations With Socioeconomic Factors
Graphs often highlight the link between ASD and socioeconomic factors. You might see that families with higher incomes have more frequent diagnoses. This raises questions about access to diagnostic resources in lower-income communities. Consider the impact of location and income on the availability of specialists. A visual representation can clearly show disparities, encouraging discussions about resource distribution. What steps can be taken to ensure more equitable access to diagnosis and treatment? Your insights could contribute to meaningful change.
Regional Variations And Trends
Examining regional differences in ASD diagnoses can be eye-opening. Some areas report higher rates, which might be influenced by local policies or healthcare practices. Have you ever wondered why some regions seem to have more cases? Viewing graphs can shed light on possible reasons, such as environmental factors or cultural awareness. As you explore these graphs, think about how regional differences might affect families and communities. What can be done to address these disparities? By engaging with these visual insights, you gain a deeper understanding of Autism Spectrum Disorder and its broader implications. Keep questioning and exploring—your curiosity can lead to valuable discoveries.
Interpreting Graphical Data
Understanding graphs related to Autism Spectrum Disorder helps in visualizing patterns and trends. These graphs can show data like diagnosis rates or age of diagnosis, aiding in better comprehension of the disorder’s impact. Interpreting such data is crucial for educators, parents, and healthcare professionals.
Interpreting graphical data about Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can be a daunting task. Yet, it’s crucial for understanding trends and making informed decisions. Graphs often provide a clear visual representation of complex data, helping you see patterns and relationships that might be missed in text. ###
Understanding Data Points And Axes
When you first look at a graph, identify the data points and axes. The x-axis might represent age groups, while the y-axis could show the number of ASD diagnoses. Knowing what each axis represents is key to understanding the story the graph tells. Data points show specific values in the dataset. They can reveal trends, like an increase in diagnoses over the years. Without this understanding, you might miss critical insights that the graph provides.
Avoiding Common Misinterpretations
Misreading graphs is a common pitfall. Sometimes, the scale of axes can be misleading. A graph may show a slight increase in data, but a zoomed-in scale might exaggerate this trend. It’s easy to jump to conclusions without fully analyzing the data. For instance, a peak in ASD diagnoses might be due to better detection methods rather than an actual increase in cases. Always question the data before forming an opinion. ###
Utilizing Graphs For Decision Making
Graphs can be powerful tools for decision making. If a graph indicates a high prevalence of ASD in a certain age group, resources can be directed to that demographic. This data-driven approach ensures that interventions are timely and effective. Consider how the data aligns with your objectives. Are there unexpected trends that could impact your strategy? Use these insights to adapt your approach and make more informed decisions. Every graph tells a story. As you interpret these stories, what new strategies could you develop? Think about how these insights can shape your actions and benefit those affected by ASD.
Future Directions In Asd Graphical Research
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) graphical research is evolving rapidly. Future directions promise exciting developments. Graphs help visualize complex data. They make it easier to understand ASD patterns. This research can transform how we approach ASD.
Innovative Visualization Techniques
New visualization techniques offer fresh insights. These techniques improve data clarity. They make complex information accessible. Interactive graphs engage users more effectively. They allow users to explore data themselves. This leads to deeper understanding of ASD.
Integration With Ai And Machine Learning
AI and machine learning enhance graphical analysis. They process vast data quickly. This helps identify patterns in ASD. Machine learning models predict future trends. AI tools personalize ASD data visualization. This aids researchers in making informed decisions.
Potential Impact On Policy And Practice
Better graphs influence policy and practice. They provide clear evidence for policymakers. This supports informed decision-making in ASD services. Improved visuals increase public awareness. They help communicate ASD findings effectively. This can lead to better support for individuals with ASD.
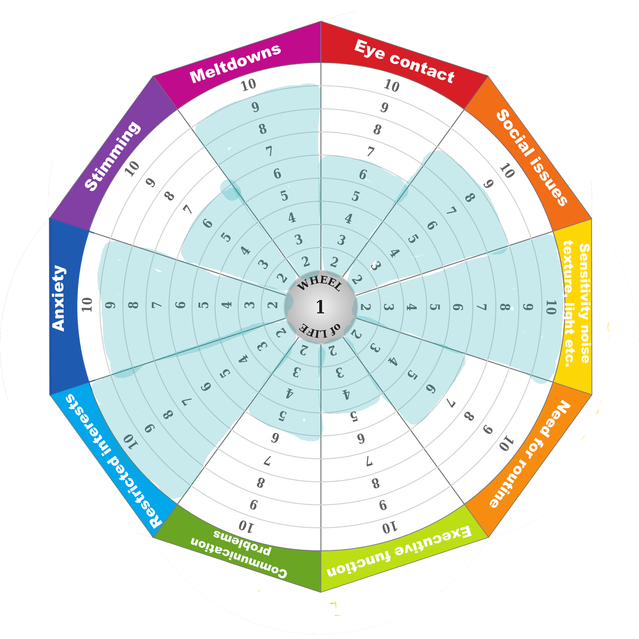
Credit: www.psychologytoday.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is 90% Of Autism Caused By?
Around 90% of autism cases are linked to genetic factors. Environmental influences might also play a role, but genetics remain the primary cause. Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) involves complex interactions between multiple genes. Understanding these genetic contributions is crucial for advancing research and developing effective interventions.
Is Autism Increasing Or Decreasing?
Autism rates are increasing globally. Improved awareness and diagnostic methods contribute to higher reported cases. Experts continue researching environmental and genetic factors potentially influencing this rise. Early intervention and support remain crucial for individuals with autism.
What Are The 12 Signs Of Autism In Adults?
Adults with autism may exhibit signs like difficulty in social interactions, repetitive behaviors, and intense focus on specific interests. They might struggle with nonverbal communication, experience sensory sensitivities, prefer routines, and have challenges in understanding emotions. Unusual speech patterns, anxiety, and difficulty adapting to changes are also common signs.
Is A High Iq Linked To Autism?
High IQ is not directly linked to autism. Autism involves a wide range of intellectual abilities. Some autistic individuals may have high IQs, while others do not. Each person’s experience with autism is unique.
Conclusion
Understanding the Autism Spectrum Disorder graph can guide better support. It highlights patterns in behavior and development. Families and educators can use this tool. It helps in planning effective strategies. Early detection and intervention become easier. The graph makes complex data simple.
It provides a clear view of individual needs. This clarity is crucial for tailored care. With informed decisions, we can improve lives. Knowledge empowers us to offer better help. The graph is a valuable resource in autism care. It bridges gaps in communication and understanding.
Let’s continue to learn and grow together.
