Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re faced with clinical terms and definitions. If you or someone you love has been diagnosed with ASD, you’re likely searching for clarity and guidance.
Let’s break down the Autism Spectrum Disorder DSM definition in a way that’s easy to understand and relate to your life. You’ll discover what ASD truly means, why it’s defined the way it is, and how this understanding can make a difference in your world.
Stay with us as we unravel the complexities of ASD and provide you with the knowledge that empowers you to navigate this journey with confidence and compassion.

Credit: www.inquiriesjournal.com
Characteristics Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental condition. It affects how people communicate and interact with others. Its characteristics vary widely. This diversity makes each individual unique. Understanding these characteristics can help in recognizing ASD.
Social Interaction Challenges
Many individuals with ASD struggle with social skills. They find it hard to make eye contact. They may prefer being alone. Understanding other people’s feelings is often difficult. These challenges affect their ability to form friendships.
Communication Difficulties
Communication can be challenging for those with ASD. Some may not speak at all. Others may repeat phrases or words. Understanding language or gestures can also be tough. These difficulties can affect daily interactions.
Repetitive Behaviors
ASD often involves repetitive actions. This includes lining up toys or repeating sounds. These behaviors can be comforting. They provide a sense of order and predictability.
Sensory Sensitivities
Many people with ASD have sensory sensitivities. Bright lights or loud sounds might be overwhelming. Certain textures can be uncomfortable. These sensitivities can affect their environment preferences.
Intense Focus On Interests
Individuals with ASD may have intense interests. They might focus deeply on specific topics. This can lead to expertise in those areas. However, it might limit conversations to those subjects.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Diagnostic Criteria
Autism Spectrum Disorder is defined by the DSM using specific diagnostic criteria. These criteria focus on social communication challenges and repetitive behaviors. Diagnosis involves observing developmental history and behavior patterns.
Understanding the diagnostic criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is essential for anyone seeking clarity on this complex condition. The DSM, or Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, offers a detailed definition that guides professionals in identifying ASD. If you’ve ever wondered how professionals diagnose autism, you’ll find the criteria surprisingly logical yet intricate. Let’s break it down. ###
Persistent Deficits In Social Communication
Social communication is a key area where individuals with ASD may face challenges. You might notice a child who rarely makes eye contact or struggles to keep a conversation flowing. These are not just quirks but significant markers that professionals consider. The DSM emphasizes difficulties in social-emotional reciprocity. This means that interactions might seem one-sided. Think about how engaging conversations rely on back-and-forth exchanges. A lack of this can be a red flag for ASD. ###
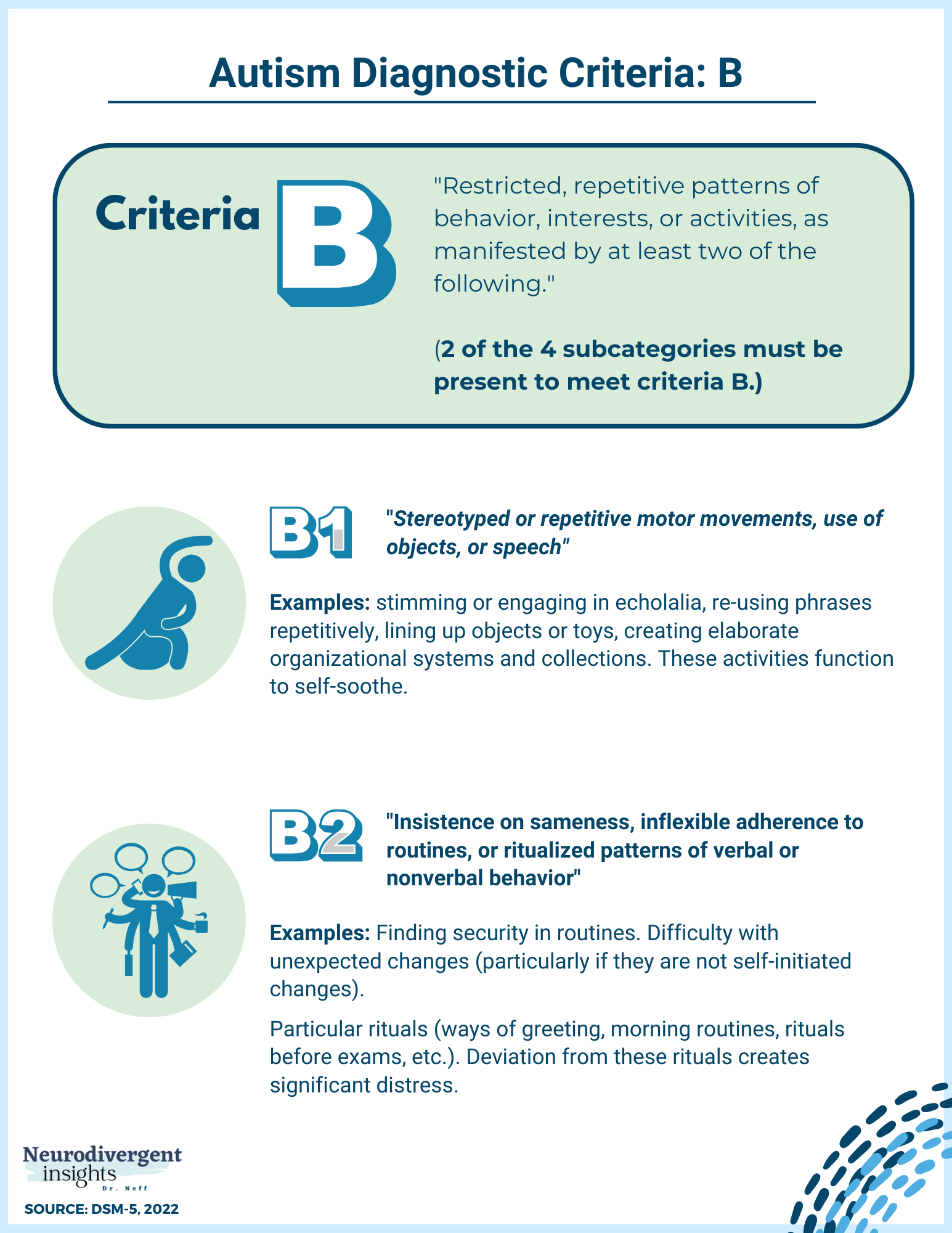
Restricted And Repetitive Patterns Of Behavior
Have you ever observed a child fixated on lining up toys or repeatedly flapping their hands? Such behaviors are more than mere habits. The DSM specifies patterns like these to help identify ASD. Repetitive behaviors can manifest in various forms, from strict routines to intense interests. It’s like being in a world where change is unsettling, and predictability offers comfort. Recognizing these patterns is crucial for diagnosis. ###
Symptoms Present In Early Development
Early detection is vital. Many parents notice signs before their child enters school. This early onset is a critical part of the DSM criteria. If you suspect ASD, consider the history of behavior and communication milestones. Did certain challenges arise before age three? Reflecting on early childhood can provide insights into whether these symptoms align with the DSM definition. ###
Significant Impairment In Daily Functioning
You might wonder how ASD impacts daily life. The DSM criteria highlight significant impairments in functioning. This covers academic, occupational, and social aspects. Imagine struggling with simple tasks that others find easy. This impairment can affect learning, making friends, and even employment. Understanding these challenges can lead to better support and strategies for those with ASD. ###
Exclusion Of Other Conditions
It’s crucial to differentiate ASD from other conditions. The DSM criteria require that these symptoms aren’t better explained by intellectual disability or global developmental delay. Have you considered if other conditions might mimic ASD symptoms? It’s essential to rule them out to ensure accurate diagnosis and support. This step is about clarity, ensuring the right approach is taken for each individual. In your journey to understand ASD, how have these criteria shaped your perspective? Recognizing these detailed markers is the first step towards empathy and effective support. Whether you’re a parent, teacher, or friend, this knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions and foster understanding.
Changes In Dsm Editions
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder requires examining its definition changes over time. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) provides this definition. Over the years, DSM editions have evolved. These changes reflect growing research and understanding. Each edition offers a refined perspective.
Changes In Dsm-iii
DSM-III was a major turning point. It introduced autism as a distinct diagnosis. This edition helped differentiate autism from schizophrenia. The focus was on early childhood symptoms. Clear criteria for diagnosis were established. This helped clinicians identify autism more accurately.
Changes In Dsm-iv
DSM-IV expanded the understanding of autism. It introduced the concept of Autism Spectrum Disorder. This term included related conditions. Asperger’s Syndrome was recognized as part of the spectrum. The changes reflected a broader approach. This edition emphasized varied symptom expressions.
Changes In Dsm-5
DSM-5 made significant adjustments. It combined several disorders into Autism Spectrum Disorder. Asperger’s and other conditions were grouped together. This aimed to simplify diagnosis. DSM-5 introduced severity levels. These levels helped assess support needs. The criteria were updated for precision.
Impact Of Dsm Changes
Each DSM change influenced diagnosis methods. Clinicians adapted to new criteria. These changes impacted treatment strategies. They shaped public awareness of autism. Families gained better understanding. The evolution of DSM reflects scientific advancement.
Common Symptoms
Understanding the common symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is crucial. These symptoms vary from person to person. Recognizing them can help in early diagnosis. Let’s explore some of the primary symptoms associated with ASD.
Communication Challenges
Many individuals with ASD face communication challenges. They might find it hard to express thoughts. Delayed speech development is often observed. Some may not speak at all. Others might repeat phrases or words. This repetition is known as echolalia. Non-verbal communication can also be difficult. Reading body language poses a challenge.
Social Interaction Difficulties
Social interaction can be tough for those with ASD. They may struggle to make eye contact. Building friendships is often challenging. Some prefer to play alone. Understanding social cues is difficult. They might not respond to their name. Empathy and understanding others’ feelings can be hard.
Repetitive Behaviors
Repetitive behaviors are common in ASD. These include hand flapping or rocking. Some develop strict routines. Changes in routines can cause distress. They might fixate on specific topics. Obsessive interests are frequent. Sensory sensitivities also occur. Loud noises or bright lights can overwhelm.
Assessment Techniques
Assessing Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) requires careful evaluation. Professionals use various techniques to understand a child’s behavior and needs. Early and accurate assessment helps in planning effective intervention strategies. Let’s explore some common techniques used in assessing ASD.
Behavioral Observations
Behavioral observations are a key part of ASD assessments. Professionals watch how a child interacts with others. They note reactions to different situations. Observations often happen in natural settings like home or school. This helps in understanding real-world behavior. Experts look for patterns in communication and social skills. They also observe repetitive behaviors. These observations guide further assessment and diagnosis.
Standardized Tests
Standardized tests provide structured ways to assess ASD. These tests compare a child’s abilities with typical development milestones. Tools like the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) are common. They offer a framework for evaluating social and communication skills. Standardized tests ensure consistency and reliability. They are essential for accurate diagnosis. Professionals use results to tailor interventions and support.
Importance Of Early Diagnosis
Recognizing Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) early is crucial. Early diagnosis can greatly improve outcomes. It helps in planning effective interventions. Families can access support services sooner. Children benefit from tailored educational plans. Understanding a child’s unique needs becomes easier.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder affects social skills and behavior. It is a developmental condition. Symptoms vary widely among individuals. Some may have challenges with communication. Others might show repetitive behaviors. Recognizing these signs early is vital.
Benefits Of Early Intervention
Early intervention provides essential support. It can improve social skills significantly. Children learn better coping strategies. They develop stronger communication abilities. This support enhances their quality of life. Early steps lead to long-term success.
Role Of Parents And Caregivers
Parents play a key role in early diagnosis. They often notice initial signs. Their observations are crucial for professionals. Caregivers should seek evaluations promptly. Early action can change a child’s life. Support from family is indispensable.
Professional Evaluations And Diagnosis
Professional evaluations are necessary for accurate diagnosis. Specialists use specific criteria. The DSM provides guidelines for diagnosis. Evaluations include observing behavior. They assess communication and interaction skills. Accurate diagnosis guides effective intervention plans.
Treatment Approaches
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can feel overwhelming, especially when trying to understand treatment options. The good news is, there are various approaches that can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. It’s crucial to remember that every individual with ASD is unique, and so are their treatment needs. Let’s explore some effective methods that can make a real difference.
Behavioral Interventions
Behavioral interventions are pivotal in ASD treatment. They focus on improving specific skills and reducing challenging behaviors. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is one of the most recognized approaches. It breaks tasks into small steps and uses rewards to encourage positive behavior.
Imagine your child learning to communicate their needs more effectively. ABA can support this by teaching simple, practical communication methods. It’s a structured approach that provides measurable outcomes, making progress tangible for you and your family.
Therapies And Support
Therapies tailored to individual needs can be life-changing. Speech therapy can enhance communication skills, while occupational therapy focuses on daily activities and sensory issues. These therapies offer practical skills that can help integrate into everyday life.
Consider joining support groups—these can be a lifeline. Sharing experiences with others in similar situations can offer insights and comfort. What could be more empowering than learning from those who truly understand your journey?
Have you ever thought about how different therapies might complement each other? Finding the right balance can unlock potential and lead to meaningful progress. Tailoring a combination of therapies could be the key to addressing specific challenges you or your loved one face.
What treatment approach resonates most with you? Remember, the goal is to enhance life skills and foster independence. With the right support, every step forward is a victory worth celebrating.
Support For Families
Families navigating Autism Spectrum Disorder can find clear guidance in the DSM definition. This helps understand symptoms, behaviors, and support needs. Finding the right resources is crucial for effective family support.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can bring unique challenges to families, but with the right support, it can also foster resilience and understanding. Navigating the complexities of ASD can be overwhelming, but you are not alone. Many resources and communities are ready to stand by you, offering guidance and encouragement every step of the way.
Understanding The Dsm Definition
The DSM, or Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, defines Autism Spectrum Disorder as a developmental disorder characterized by difficulties in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. Knowing this helps families understand the unique needs of their loved ones.
Emotional Support Networks
Finding emotional support is crucial. You might benefit from connecting with others who share similar experiences. Local support groups and online forums can be lifelines, offering you empathy, advice, and a sense of community.
Educational Resources
Educating yourself and your family about ASD can empower you. Look for books, webinars, and workshops that provide insights into autism. Schools and therapists can also offer valuable information to enhance your understanding.
Practical Strategies For Daily Life
Implementing practical strategies in your daily routine can make a significant difference. Consider creating a structured environment with clear routines. Visual schedules and social stories can help your child anticipate and understand daily activities.
Professional Guidance
Professional guidance is often necessary. Seek out therapists and specialists who can offer personalized strategies tailored to your family’s needs. Their expertise can help you develop skills to manage behavioral challenges effectively.
Building A Supportive Environment
Creating a supportive home environment is essential. Encourage open communication, celebrate small victories, and promote acceptance. This can help build a nurturing space where your child feels safe and valued.
Financial Assistance And Resources
Financial challenges may arise, but there are resources available. Research grants, government programs, and non-profit organizations that offer financial assistance for therapies and other needs related to ASD.
Encouraging Self-advocacy
As your child grows, encourage self-advocacy. Teach them to express their needs and preferences. This not only boosts their confidence but also prepares them for independence in adulthood.
Reflecting On Your Journey
Take time to reflect on your journey. What lessons have you learned? How has your family grown stronger? Sharing your story can inspire others and reinforce your own resilience. Does your family have unique strategies that have helped you? Sharing your insights can provide comfort and guidance to others facing similar challenges.
Future Developments
The future of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is rich with possibilities. Researchers are working hard to understand this complex condition. New advancements may soon change how we view and treat ASD. These developments focus on better research and improved tools. They aim to provide clearer insights and support for individuals with ASD.
Research Innovations
Scientists are exploring new ways to study ASD. They use advanced technologies to learn about the brain. These innovations help identify patterns linked to autism. Genetic research is another key area. It uncovers the role of genes in autism development. This knowledge can lead to targeted therapies. Researchers also focus on environmental factors. These studies examine how surroundings influence ASD symptoms.
Improved Diagnostic Tools
Better diagnostic tools are crucial for early detection. New methods aim to identify ASD at a younger age. Early diagnosis can lead to more effective interventions. Technology plays a significant role here. Artificial Intelligence (AI) helps in analyzing behavioral patterns. This assists in providing accurate diagnoses. Improved tools also support personalized treatment plans. They ensure that interventions meet individual needs.
Credit: neurodivergentinsights.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Dsm-5 Definition Of Autism Spectrum Disorder?
The DSM-5 defines autism spectrum disorder as a developmental condition affecting communication and behavior. It includes challenges with social interaction, repetitive behaviors, and restricted interests. Symptoms begin early in childhood and impact daily functioning. Diagnosis requires assessment of social communication and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior.
What Is The Official Definition Of Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental condition characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and behavior. It encompasses a range of symptoms and abilities. Early diagnosis and intervention can help manage ASD effectively, improving life quality for those affected.
What Is The Legal Definition Of Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is legally defined as a developmental disability affecting communication, behavior, and social interaction. It involves a range of symptoms and abilities. Each individual with ASD may experience different challenges and strengths. Diagnosis typically requires professional evaluation and assessment based on specific diagnostic criteria.
What Is The Dsm 3 Definition Of Autism?
DSM-III defined autism as a pervasive developmental disorder impacting communication and social interactions. It included repetitive behaviors and restricted interests. Diagnosis required symptoms before age 3. This definition laid the groundwork for understanding autism in clinical settings.
Conclusion
Understanding the DSM definition of Autism Spectrum Disorder is crucial. It aids in recognizing diverse symptoms. Helps in seeking appropriate support. Early intervention can make a difference. Families and caregivers benefit from awareness. Professionals can tailor strategies effectively. Society gains empathy and better inclusion.
This knowledge empowers everyone involved. Spreading awareness leads to acceptance. Acceptance fosters a supportive community. Every step counts in building understanding. Let’s continue learning and sharing insights. Together, we can create a caring environment. For individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Supporting each journey towards a fulfilling life.
